Table of Contents
Ecommerce Business Models Explained
This is far from an exhaustive or comprehensive list, but this page illustrates some of the most common ecommerce business models and how they work.
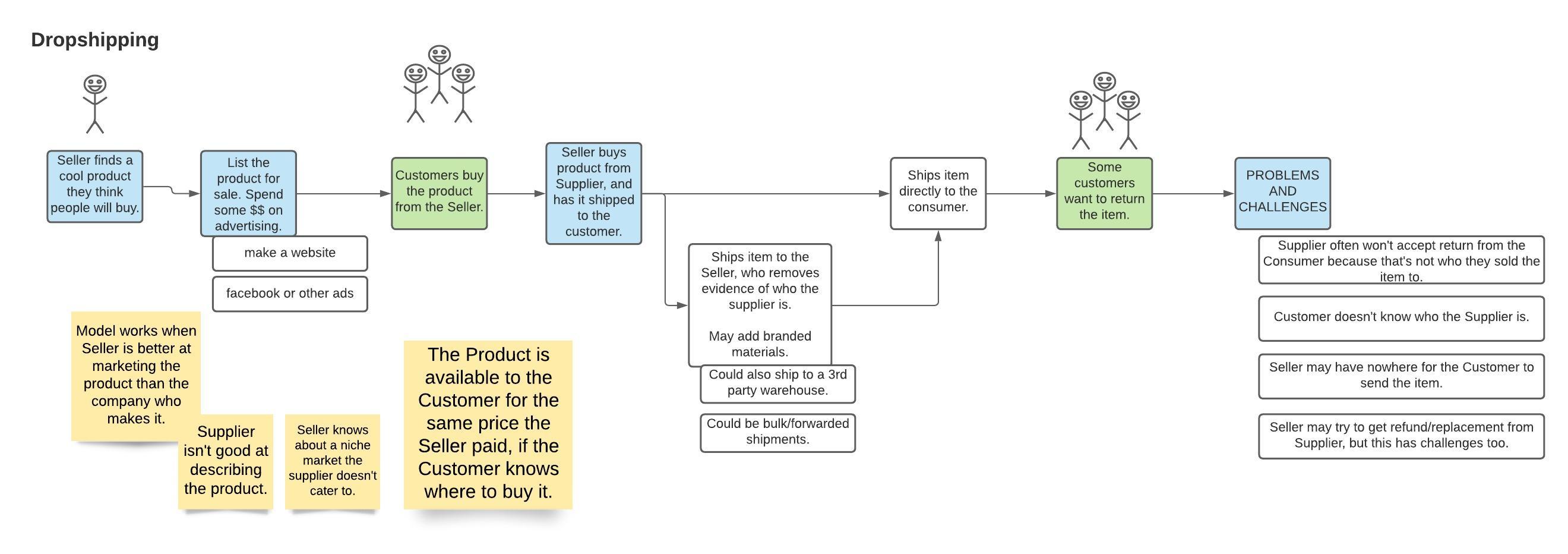
Dropshipping Business Model
Basic idea: the seller is listing inventory for sale they don't actually own. They buy the inventory once a customer pays, and then ship it to the customer.
Arbitrage (aka OA or RA)
Basic idea: Seller buys inventory at a discount from a retailer or online store, and then sells it at a higher price somewhere else.
Many 3PLs charge extra or refuse to handle arbitrage. This article explains whyplugin-autotooltip__default plugin-autotooltip_bigChallenges with Online Arbitrage
You may find many 3PLs and prep centers don't work with OA, or they charge extra. This article explains why, with the goal of helping you get better deals and more efficient service.
Delivery and packaging are unpredictable.
Wholesale
Basic idea: Seller negotiates a deal with a wholesaler, distributor, or manufactuer to purchase large quanitites of products in bulk at a discount. The seller then sells them online.
Wholesale can have certain advantagesplugin-autotooltip__default plugin-autotooltip_bigAdvantages of Wholesale vs. Private Label
First, let’s understand the difference between wholesale FBA and PL.
PL = Private Label and in PL we create a completely new brand and handle everything from getting it manufactured to handling shipments to listing to ranking. over private label, especially getting started.